Language
 Directory
Directory
Part 2
The Canon of the Bible

What Is Canon?
The canon of the Bible refers to the collection of books widely recognized and accepted as divinely inspired and authoritative within the Christian faith. The content of canon law may vary slightly from denomination to denomination and religious tradition to religious tradition, but generally includes both the Old and New Testaments.
The Old and New Testaments
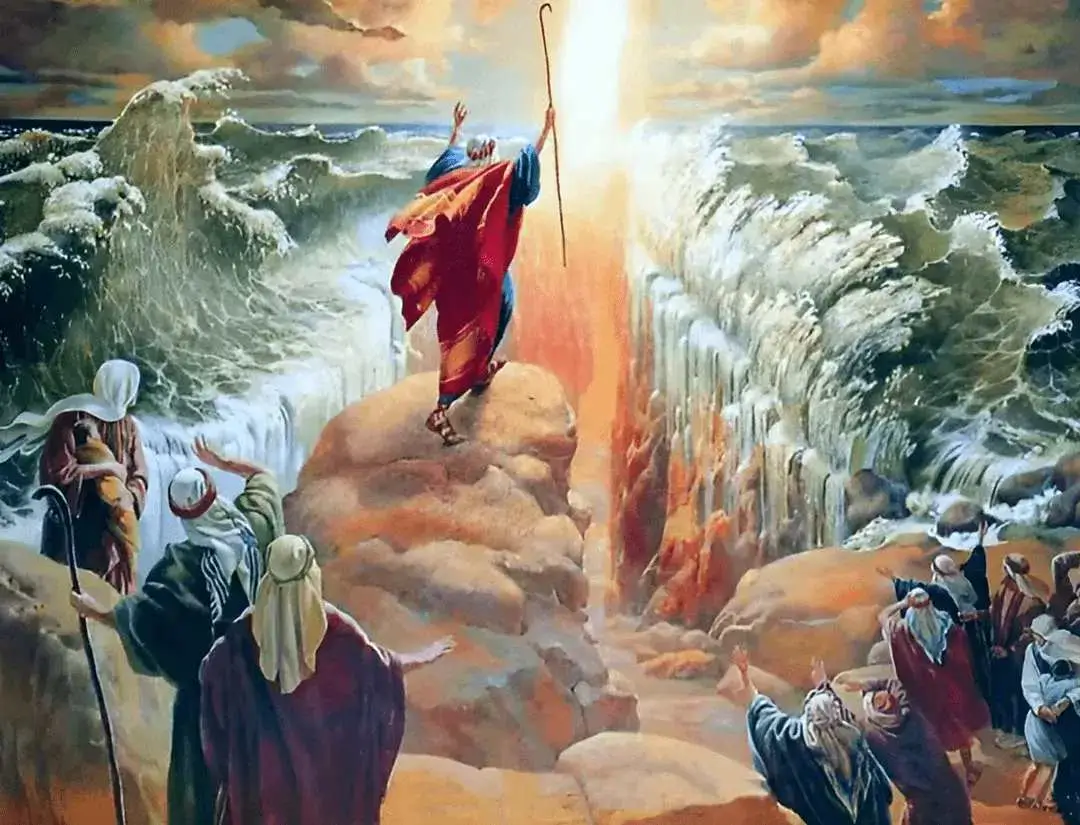
Old Testament: This is the first part of the Christian Bible, also known as the Hebrew Bible or Tanakh. It includes 39 books from Genesis to Malachi, covering the origins of the world, the history of the Jewish people, laws, poetry, and prophetic literature.
New Testament: This is the second part of the Christian Bible and focuses on the life, teachings, death, and resurrection of Jesus Christ, as well as guidance for believers' lives. It includes the four Gospels, Acts of the Apostles, Pauline Epistles, General Epistles, and the Book of Revelation.
The Role of the Canon
The process of forming the canon in early Christian history was relatively lengthy and complex, involving multiple councils and discussions. Eventually, books that were widely accepted and recognized as authoritative were included in the canon, becoming a widely accepted and revered collection of biblical texts within the Christian tradition. The formation of the canon played a significant role in establishing faith, doctrine, and regulating religious practices.




 Previous
Previous